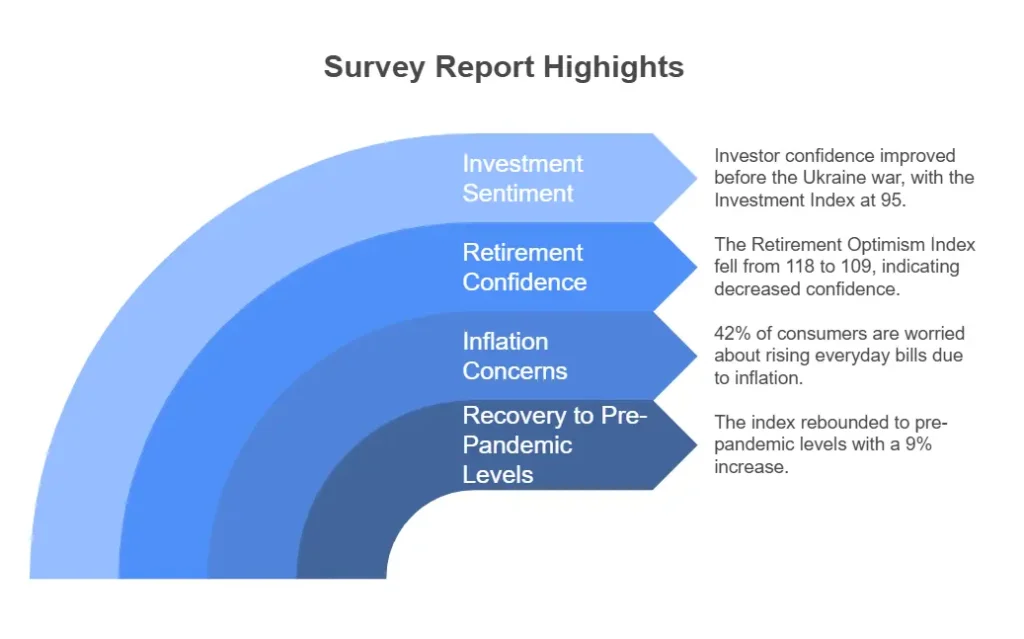
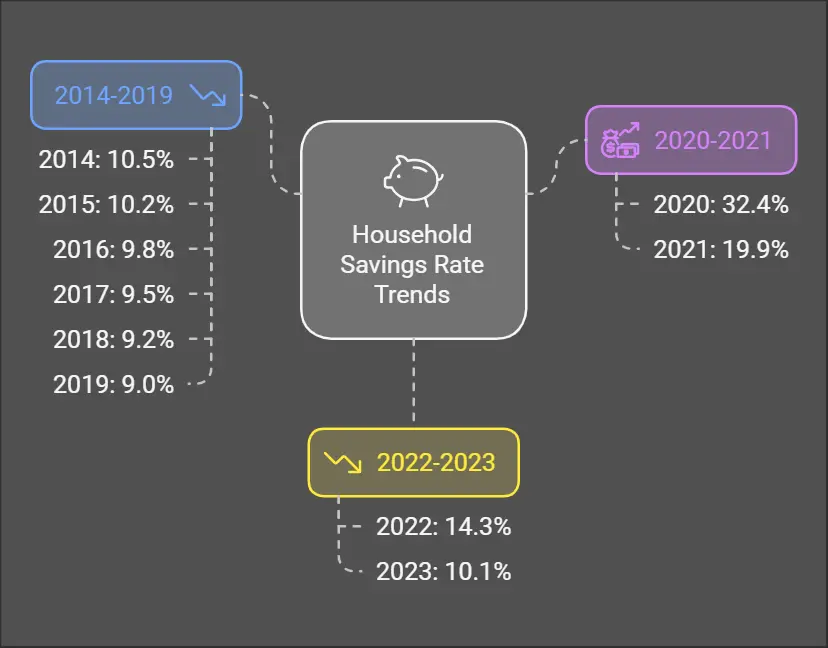
The savings rates for 2024 have fluctuated but generally indicate a normalization: Q1 2024: 14.7%, Q2 2024: 12.7% and Q3 2024: 14.1%. These figures are in line with pre-pandemic levels which hovered around 10% from 2014-2019. The convergence of the Irish household savings rate to pre-pandemic levels is a positive sign of economic recovery and restored consumer confidence. However, it also brings to the forefront the importance of strategic financial planning for households amid inflation concerns.
However, the simultaneous rise in inflation presents a new set of challenges. As of November 2024, Ireland’s annual inflation rate stands at 1.0%, which is relatively low but still a concern for households and policymakers. Inflation affects purchasing power, meaning that the money saved today may have less value in the future if prices for goods and services rise.
The European Central Bank (ECB) has also taken actions that impact the economic environment, such as adjusting key interest rates to manage inflation and support economic recovery. While lower interest rates can stimulate spending and investment, they can also contribute to inflation if not carefully managed.
Both individuals and policymakers must remain vigilant:
Households should focus on financial strategies that hedge against inflation and make their savings work effectively.
Policymakers need to balance stimulating economic growth with measures to control inflation, ensuring long-term economic stability.
By addressing these challenges proactively, Ireland can continue on a path of sustainable economic growth while safeguarding the financial well-being of its citizens. The interplay between savings rates and inflation will remain a critical area to watch in the coming months and years.